Decoding Handrail Regulations: Your Guide to Safe Steps
Ever tripped on the stairs? It's a surprisingly common – and potentially dangerous – mishap. Handrails, often overlooked, are crucial safety features, and their design and installation are governed by specific building codes. These handrail code requirements for steps aren't just bureaucratic red tape; they're designed to prevent falls and ensure accessibility for everyone.
Understanding these regulations can be tricky. This guide aims to demystify handrail requirements, breaking down the essential elements you need to know to ensure your steps are safe and compliant. Whether you're a homeowner, a builder, or just someone curious about building safety, this guide will help you navigate the world of handrail regulations.
Historically, building codes, including those for handrails, have evolved from practical experience and the need to address common safety hazards. Early codes were often localized and inconsistent. The rise of national and international building codes has led to more standardized handrail requirements, emphasizing accessibility and universal design principles.
The importance of adhering to handrail standards cannot be overstated. Handrails provide essential support, helping people maintain balance while ascending or descending stairs. This is particularly critical for children, the elderly, and individuals with mobility impairments. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in accidents, legal liabilities, and costly renovations.
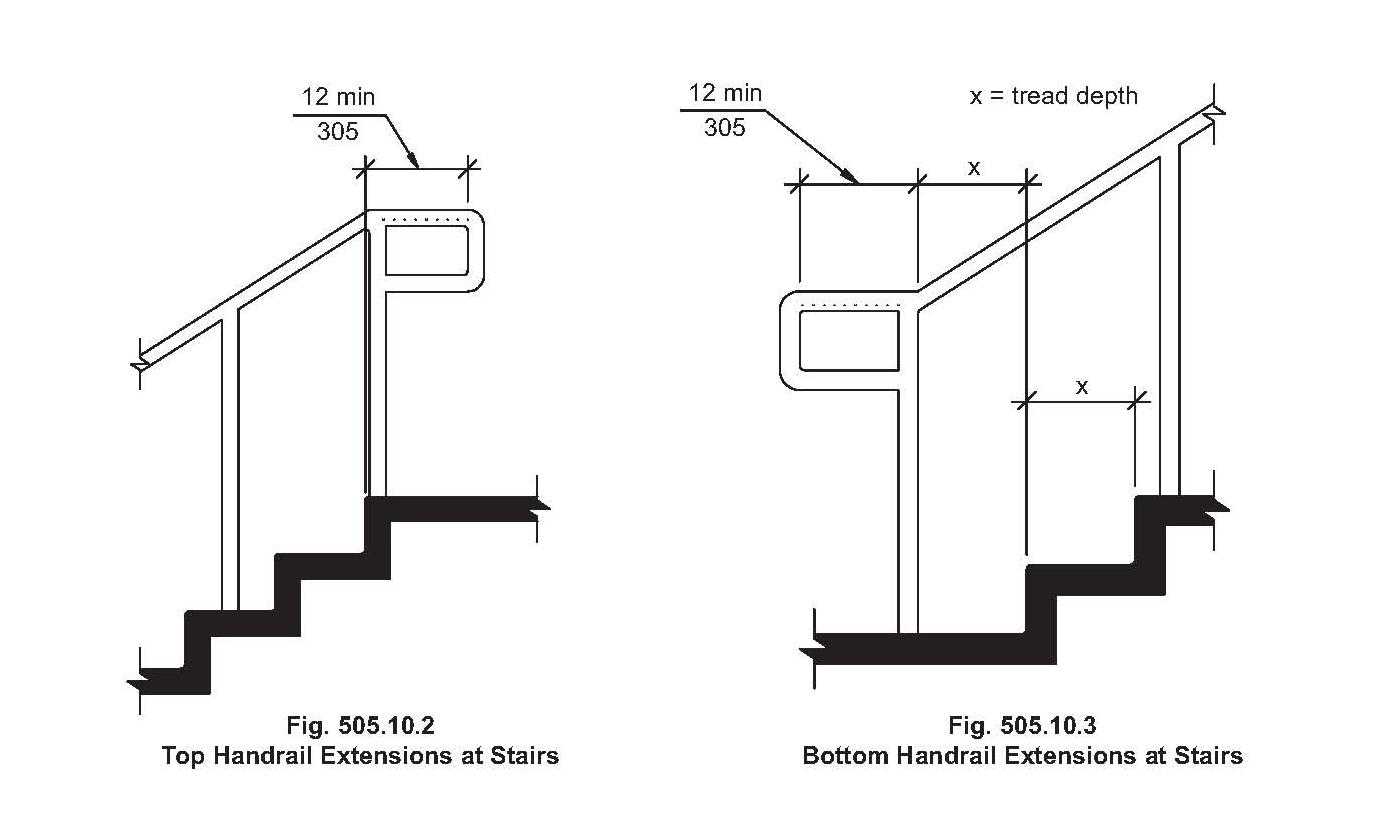
One of the most common issues related to handrail compliance is incorrect height. Building codes typically specify a specific range for handrail height, measured vertically from the nosing of the stair tread. Other common issues include inadequate handrail extensions at the top and bottom of the stairs, incorrect handrail graspability, and the use of unsuitable materials.
Handrail codes specify requirements for various aspects of handrail design, including height, graspability, continuity, and extensions. Graspability refers to the ease with which a handrail can be gripped. Codes often dictate a specific diameter or cross-sectional profile to ensure a comfortable and secure grip.
Benefits of adhering to handrail codes include enhanced safety, improved accessibility, and increased property value. By providing a secure handhold, handrails significantly reduce the risk of falls. They also ensure that people of all ages and abilities can safely navigate stairs. Compliant handrails can also boost a property's value by demonstrating a commitment to safety and accessibility.
Creating a compliant handrail system involves careful planning and execution. Begin by researching the specific handrail code requirements in your jurisdiction. Consult with a qualified builder or architect to ensure proper interpretation and implementation of the code. Finally, inspect the installed handrails to verify compliance with all relevant regulations.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Standardized Handrail Codes
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Improved Safety | Potential Increased Costs |
| Enhanced Accessibility | Complexity of Regulations |
| Reduced Liability | One-size-fits-all approach may not always be ideal |
Best practices for implementing handrail codes include using durable and weather-resistant materials, ensuring proper handrail clearance from walls and other obstructions, and providing continuous handrails on both sides of stairways whenever possible.
Real-world examples of handrail code compliance can be found in public buildings, schools, and commercial spaces. These buildings are typically subject to rigorous inspections to ensure adherence to all applicable building codes, including handrail requirements.
Common challenges related to handrail code compliance include navigating complex regulations, finding qualified contractors, and dealing with site-specific constraints. Solutions to these challenges include seeking expert advice, utilizing prefabricated handrail systems, and engaging in early planning to address potential issues.
FAQs about handrail codes often address topics like handrail height requirements, permissible materials, and exceptions to the code. Consulting local building departments or accessibility specialists can provide answers to specific questions.
Tips and tricks for ensuring handrail compliance include using a handrail height gauge during installation, verifying handrail graspability with a simple grip test, and documenting all aspects of handrail construction for inspection purposes.
In conclusion, understanding and adhering to handrail code requirements for steps is not merely a legal obligation; it's a crucial step in creating a safe and accessible environment. From preventing falls to ensuring inclusivity, compliant handrails play a vital role in protecting everyone who uses stairs. By prioritizing handrail safety and following the guidelines outlined in this comprehensive guide, we can contribute to a more accessible and secure built environment. Take the time to review your existing handrails or plan your new staircase with these code requirements in mind. It's a small investment that can make a world of difference in safety and accessibility for everyone.
Finding healthcare in eldersburg md a guide to local options
Missouri eclipse a celestial spectacle you wont want to miss
Finding the perfect paint sherwin williams store near me

international building code for handrails | Innovate Stamford Now

Building Regulations For Stair Handrails | Innovate Stamford Now

Disabled access handrail guide and Part M Regulations | Innovate Stamford Now

Handrail Indoor Railings at Scott Dempsey blog | Innovate Stamford Now

osha requirements for handrails on stairs | Innovate Stamford Now

Steel Handrail Thickness at Wilma Steppe blog | Innovate Stamford Now
Ada Handrail Code Requirements at Krystal Hairston blog | Innovate Stamford Now

code requirements for handrails on steps | Innovate Stamford Now

Deck Railing Code Requirements at Rodney Nunnally blog | Innovate Stamford Now

Are Handrails Required On Both Sides Of Exterior Stairs at Brian | Innovate Stamford Now

Residential Stair Codes Rise Run Handrails Explained | Innovate Stamford Now

code requirements for handrails on steps | Innovate Stamford Now

Outdoor Railing Design Ideas at Allen Courtois blog | Innovate Stamford Now

IBC Handrail International Building Code handrail railing guard | Innovate Stamford Now

What Is Building Code For Stair Railing at Heather Ridout blog | Innovate Stamford Now