Mastering Metric Bolt Torque Specs in Aluminum: A Comprehensive Guide
Are you tired of stripped threads and loose bolts in your aluminum projects? Properly tightening metric bolts in aluminum is crucial for achieving structural integrity and preventing failures. This seemingly simple task involves a nuanced understanding of torque specifications and the unique properties of aluminum.
Fastening metric bolts into aluminum isn't as simple as turning the wrench until it feels "tight enough." Over-tightening can strip threads or even crack the aluminum, while under-tightening leads to loose joints and potential component failure. Understanding the appropriate tightening values for metric bolts in aluminum, commonly referred to as torque specifications or torque specs, is the key to a secure and lasting assembly. This involves considering factors such as bolt size, thread pitch, and lubricant use.
Torque specifications represent the rotational force applied to a fastener, measured in units like Newton-meters (Nm) or pound-feet (lb-ft). These specifications are carefully engineered to ensure the bolt is tightened enough to create the necessary clamping force without exceeding the aluminum's yield strength. While general guidelines exist, always consult the manufacturer's specifications for your specific application, as different aluminum alloys and bolt grades have varying torque requirements.
Historically, determining the appropriate tightening force was largely based on experience and "feel." However, as engineering precision became increasingly important, particularly in fields like aerospace and automotive, the need for standardized and reliable torque specifications grew. Today, sophisticated tools and techniques, including torque wrenches and digital torque analyzers, ensure consistent and accurate tightening, minimizing the risk of joint failure.
The importance of correct torque specs for metric bolts into aluminum cannot be overstated. Properly torqued bolts ensure the integrity of the joint, preventing loosening under vibration or load. This is especially critical in applications subject to dynamic forces, such as engine components or structural elements. Correctly applied torque specifications also contribute to the longevity of the assembly, preventing premature wear and tear caused by movement or stress.
Understanding metric bolt torque values requires understanding the metric system and the various grades of bolts. Bolt grades are indicated by markings on the bolt head and correspond to the bolt's tensile strength. A higher grade bolt typically requires a higher torque value. Using the incorrect torque value for a specific bolt grade can lead to either stripping the threads in the aluminum or an insufficient clamping force.
One benefit of adhering to correct torque specs is preventing damage to the aluminum. Over-tightening can strip the relatively soft threads of aluminum, leading to costly repairs or even component replacement. Conversely, correct tightening prevents the bolt from loosening, maintaining the integrity of the assembly.
Another benefit is ensuring the intended clamping force. This force is essential for holding parts together securely, preventing movement or slippage. Correct torque application ensures the joint can withstand the intended loads and stresses, preventing failures.
Finally, proper torque specification application contributes to the overall longevity of the assembly. By minimizing stress on the aluminum and the bolts, proper tightening prevents premature wear and fatigue, extending the service life of the components.
A simple action plan for tightening metric bolts into aluminum involves: 1) Identify the bolt grade and size. 2) Consult a reliable torque chart for the recommended torque specification. 3) Select the appropriate torque wrench and set it to the specified value. 4) Apply lubricant to the threads and under the bolt head. 5) Tighten the bolt in a smooth, controlled motion until the wrench clicks or reaches the desired torque.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Torque Specs
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Prevents over-tightening and damage | Requires specialized tools (torque wrench) |
| Ensures consistent and reliable tightening | Can be time-consuming for large assemblies |
| Increases the lifespan of the assembly | Requires accurate identification of bolt grade |
Best Practices: 1) Always use a calibrated torque wrench. 2) Clean the threads and mating surfaces before assembly. 3) Apply lubricant. 4) Tighten bolts in a cross pattern for even clamping force. 5) Re-torque after a certain period, especially in critical applications.
Challenges and Solutions: 1) Inconsistent aluminum quality - Solution: Test the aluminum before assembly. 2) Difficulty accessing bolts - Solution: Use angled torque wrenches. 3) Temperature variations affecting torque - Solution: Compensate for temperature using appropriate charts.
FAQs: 1) What is torque? 2) How do I choose the right torque wrench? 3) What are the different types of torque wrenches? 4) Why is lubrication important? 5) How often should I calibrate my torque wrench?
Tips and Tricks: Consider using a torque angle meter for more precise tightening. Use anti-seize lubricant to prevent galling. Keep a log of torque values for critical applications.
In conclusion, understanding and applying the correct torque specifications for metric bolts in aluminum is paramount for creating strong, reliable, and long-lasting assemblies. By following the guidelines outlined in this guide, you can avoid costly mistakes and ensure the integrity of your projects. Mastering this essential skill empowers you to build with confidence, knowing that your aluminum assemblies will withstand the test of time and perform as intended. Take the time to research, invest in the proper tools, and develop a consistent process for tightening metric bolts into aluminum. Your projects will benefit from the increased reliability and longevity that proper torque control provides, leading to a higher quality and more professional finished product. This knowledge is essential for anyone working with aluminum, from DIY enthusiasts to professional engineers, making your projects safer, stronger, and more dependable.
Exploring the enigma of farrow ball black blue
Anticipation builds for snapping into love episode 14
Wells fargo bank accounts for kids a parents guide

Grade 8 Fine Thread Bolt Torque Chart | Innovate Stamford Now

Torque Specs For 516 Bolt | Innovate Stamford Now

U Bolt Torque Specs Semi Truck at Debra Mcalister blog | Innovate Stamford Now

Torque Setting For M8 Bolt | Innovate Stamford Now

Sti Pressure Plate Torque Specs at Everett Schulte blog | Innovate Stamford Now
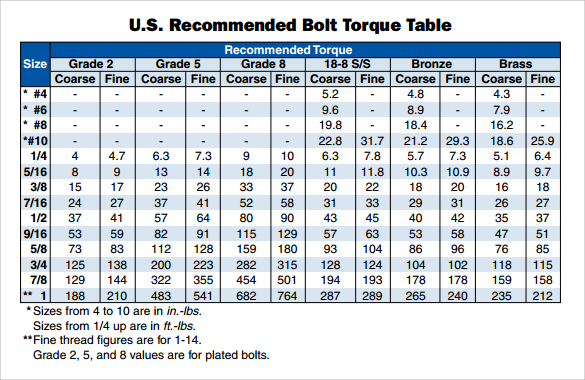
Max Torque For 716 Bolt | Innovate Stamford Now

What Are The Torque Specs For Clutch Bolts at Shannon Reichert blog | Innovate Stamford Now

Torque Setting For M10 Stainless Steel Bolts | Innovate Stamford Now

Stainless Bolt Torque Chart | Innovate Stamford Now

Aluminum Bolt Torque Chart | Innovate Stamford Now

Buy Useful Magnets Comprehensive Reference Tightening Torque Chart for | Innovate Stamford Now

Bolt Torque Chart Grade 8 | Innovate Stamford Now

Torque Specs For Sae Bolts Chart | Innovate Stamford Now

Grade 8 Metric Bolt Torque Chart | Innovate Stamford Now

Aam 115 Axle Flange Bolt Torque at Lucille Reed blog | Innovate Stamford Now